The European Space Agency Business Incubation Centre (ESA BIC) network is a thriving ecosystem designed to support entrepreneurs who leverage space technology to create innovative solutions. While the name might suggest a focus solely on “rocket science”, the reality is that anyone with a link to space technology can apply. This opens doors for a wide range of applications: from agriculture and healthcare, to logistics and environmental monitoring.
Supporting Start-Ups at ESA BICs
The ESA BICs are equipped with facilities to nurture start-ups. These include office spaces, meeting rooms, and laboratories equipped for testing and development. A typical day at an ESA BIC location is full of activity. Entrepreneurs work on their projects, attending workshops, and engaging in brainstorming sessions within their teams. The environment is collaborative, with a sense of camaraderie amongst the start-ups. Besides the smell of fresh coffee, smells of metal, solder, 3D-printed materials can be noticed when entering the building.
Business incubation centres such as ESA BICs, are beneficial for fostering innovation and economic growth. They provide the necessary support for start-ups to transition from idea to market-ready product. By offering financial backing, technical expertise, and business development assistance, ESA BICs help bridge the gap between cutting-edge space technology and its applications. What makes the BICs unique is their link to space solutions and acting as a first customer by procuring the first product or prototype of its start-ups.
Providing facilities
Entrepreneurs in the ESA BIC network gain access to specialised facilities that enable the testing and development of their innovations. For example in Bremen, the ESA BIC offers proximity to a drop tower, where companies can conduct (zero-G) experiments in collaboration with ZARM, a rare opportunity outside of space itself. This facility allows entrepreneurs to observe how their technologies function under microgravity conditions, providing invaluable data that can propel developments for space applications. The lab spaces surrounding the drop tower support these experiments, making Bremen a critical hub for testing space tech.
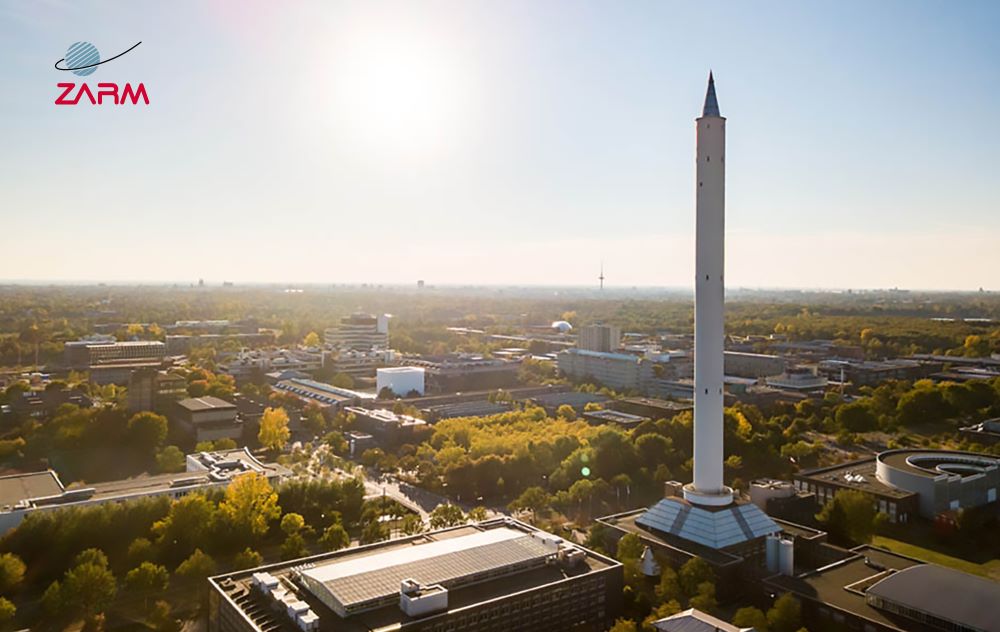

ZARM Drop Tower. Credits: European Space Agency
Further up north, ESA BIC Sweden start-ups have the opportunity to benefit from Sweden’s unique ecosystem for space innovation. There, the proximity to Esrange Space Center, owned and operated by Swedish Space Corporation (SSC), plays an important role. Through its office in Luleå, ESA BIC Sweden has a natural connection to the region’s space industry. The relationship with SSC and the Esrange Space Center offers exciting opportunities for start-ups in the space sector.
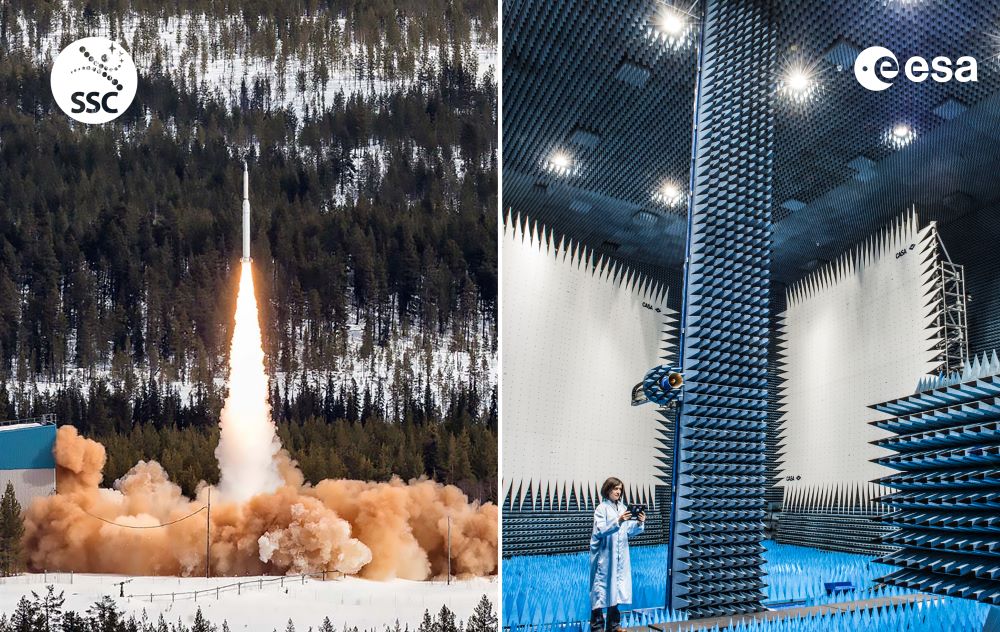

Left side: Esrange Space Center launch site. Credits by Esrange Space Center. Right side: Startups at ESA BIC Noordwijk receive, next to financial and business support, also technical support ESA ESTEC
In the Netherlands, ESA ESTEC in Noordwijk stands as the technical heart of ESA, with a vast array of testing facilities in immediate proximity to the local ESA BIC. One of its close-by neighbours is a drone airfield (Unmanned Valley), for aerial testing. And in Bavaria, ESA ESOC’s connection with the German Aerospace Center (DLR) in Darmstadt enriches the offerings of the BIC, fostering collaboration across missions and technology trials that drive forward Europe’s role in space.
Skills development, mentorship, and networking
One of the key benefits of being part of the ESA BIC network is access to a wealth of resources aimed at skills development. Start-ups receive mentorship from industry experts, technical support from ESA specialists, and business coaching to support them during their entrepreneurial journey. Next to that, there are networking opportunities the whole year around, allowing entrepreneurs to connect with potential investors, partners, and customers, as well as other start-ups facing similar challenges.
The latter is an aspect that makes being part of an incubator a special place: going through challenges, small or large, and sharing those with other entrepreneurs can create a bond and a feeling of recognition. Anyone can learn from anyone.
The ESA BIC network’s reach
The ESA BIC network contains 32 ESA BICs in 22 Participating States (covering over 100 locations as many ESA BIC hubs operate through multiple regional branches), each offering tailored support. It provides a unique combination of local support and access to a broader European ecosystem, enabling start-ups to tap into a pool of knowledge, resources, and market opportunities.
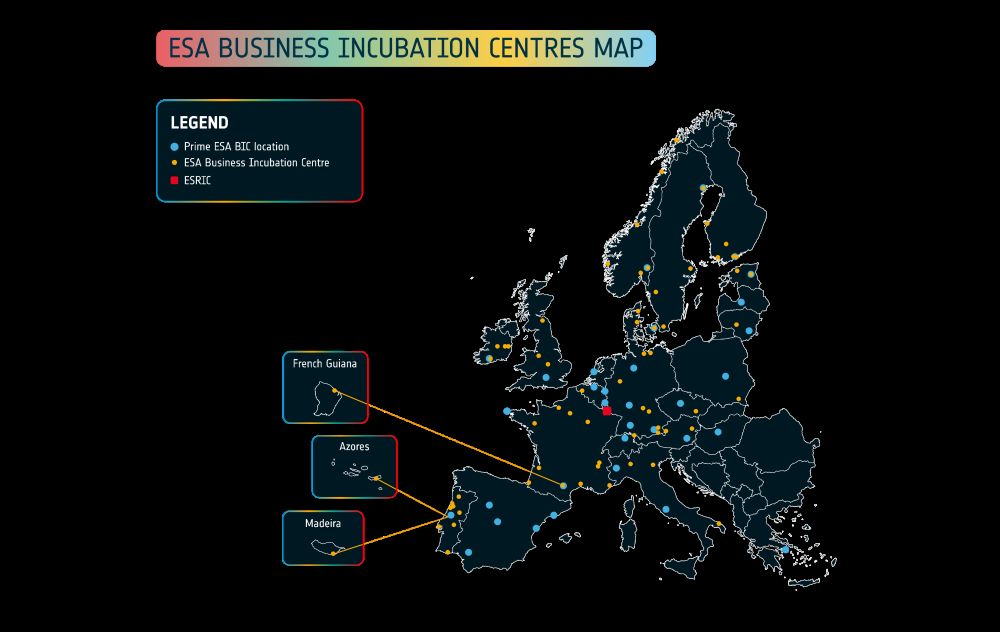
Map of ESA Business Incubation Centres in Europe (Credits: ESA Commercialisation Gateway)
It is a dynamic and supportive environment where aspiring entrepreneurs can thrive. With access to top-notch facilities, expert mentorship, and a strong community, start-ups are well-equipped to turn innovative ideas into successful businesses.
If you are interested in applying for ESA BIC, consult the application deadlines from the ESA BIC in your area by clicking on the button below.
Check ESA BICs hereThis article was written for the occasion of the 20 years anniversary of ESA BIC in Europe.
For the full overview of this celebration, go to the LinkedIn group by clicking on the button below.









